Levofloxacin Hydrochloride Capsule Instructions
Please read the instructions carefully and use under the guidance of a doctor
Prohibited for food and feed processing
caveat:
In all age groups, fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin hydrochloride, can lead to an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture. This risk is further increased in elderly patients over 60 years of age, patients receiving glucocorticoid therapy, and patients receiving kidney transplantation, heart transplantation, or lung transplantation.
Fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin hydrochloride, can worsen myasthenia in patients with myasthenia gravis. Levofloxacin hydrochloride should be avoided in patients with a known history of myasthenia gravis.
【Drug Name】
Generic name: Levofloxacin Hydrochloride Capsules
Commodity name: Lifandi
English name: Levofloxacin Hydrochloride Capsules
Chinese Pinyin: Yansuan Zuoyangfushaxing Jiaonang
【Ingredients】
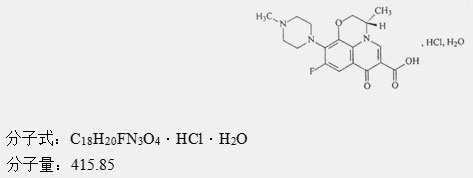
Chemical name: (—)-(S)- 3-methyl-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyridine And [1,2,3-de]-[1,4]benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid hydrochloride monohydrate.
Its chemical structure:
【Properties】
This product is a hard capsule, and the content is white or off-white powder.
【Indications】
Applicable to those caused by sensitive bacteria:
1. Urogenital infections, including simple, complicated urinary tract infections, bacterial prostatitis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae urethritis or cervicitis (including those caused by enzyme-producing strains).
2. Respiratory tract infections, including acute onset of bronchial infections caused by sensitive gram-negative bacilli and lung infections.
3. Gastrointestinal infections are caused by Shigella, Salmonella, Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Hydrophilic Aeromonas, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, etc.
4. Typhoid fever.
5. Bone and joint infections.
6. Skin and soft tissue infections.
7. Systemic infections such as sepsis.
【specification】
0.1g (calculated as C 18 H 20 FN 3 O 4 )
【Dosage】
oral. Common dosage for adults:
1. Bronchial infection, lung infection: 0.2g once, 2 times a day, or 0.1g once, 3 times a day, the course of treatment is 7 to 14 days.
2. Acute simple lower urinary tract infection: 0.1g once, twice a day, treatment course for 5-7 days; complicated urinary tract sensation
Staining: 0.2g once, 2 times a day, or 0.1g once, 3 times a day, the course of treatment is 10 to 14 days.
3. Bacterial prostatitis: 0.2g once, twice a day, the course of treatment is 6 weeks.
The usual dosage for adults is 0.3~0.4g per day, divided into 2~3 times. If the infection is severe or the pathogen is less susceptible to infection, the therapeutic dosage of Pseudomonas bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa can also be used. Increase to 0.6g a day, divided into 3 servings.
【Adverse reactions】
This product is levofloxacin hydrochloride, and its active ingredient is levofloxacin. The related information of levofloxacin reported in the literature is as follows:
1. Serious and other important adverse reactions
The following serious and other important adverse reactions are detailed in the [Precautions]: tendinitis and tendon rupture, worsening of myasthenia gravis, hypersensitivity, other severe and sometimes fatal reactions, liver toxicity, central nervous system effects, difficult Clostridium-related diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, QT interval prolongation, musculoskeletal disease in pediatric patients, blood glucose disorders, photosensitivity/phototoxicity, and the production of resistant bacteria.
It has been reported that the use of quinolones (including levofloxacin) may cause crystaluria and tubular urine. Therefore, for patients receiving levofloxacin treatment, proper hydration should be maintained to prevent the formation of highly concentrated urine.
2. Clinical trial experience
Since clinical trials are completed under different conditions, the adverse reaction rate of a drug observed in clinical trials cannot be directly compared with the adverse reaction rates of other drugs in clinical trials, and may not necessarily reflect the adverse reactions in actual applications. rate.
The data described below reflects the combined exposure to levofloxacin in 7,537 patients in 29 phase III clinical trials. The average age of the study population was 50 years old (about 74% of the population was less than 65 years old), of which 50% were male, 71% were white, and 17% were black. Patients are treated with levofloxacin for a wide range of infectious diseases (see indications). The dose of levofloxacin received by patients is 750 mg once daily, 250 mg once daily, or 500 mg once or twice daily. The course of treatment is usually 3 to 14 days, and the average course of treatment is 10 days.
The overall incidence, type, and distribution of adverse reactions were similar in patients taking levofloxacin 750 mg once daily, 250 mg once daily, or 500 mg once or twice daily. A total of 4.3% of patients discontinued levofloxacin due to adverse drug reactions. Among patients receiving 250 mg and 500 mg daily doses, this proportion was 3.8%; among patients receiving 750 mg daily doses, this proportion was 5.4 %. In patients receiving 250 mg and 500 mg daily doses, the most common adverse drug reactions leading to discontinuation were gastrointestinal reactions (1.4%), mainly nausea (0.6%), vomiting (0.4%), and dizziness (0.3%). %) and headache (0.2%). The most common adverse drug reactions leading to discontinuation in patients receiving 750 mg daily doses were gastrointestinal reactions (1.2%), mainly nausea (0.6%), vomiting (0.5%), dizziness (0.3%) and Headache (0.3%).
In the following table (Table 1 and Table 2), the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥1% of patients receiving levofloxacin, and the adverse reactions that occurred in 0.1 to <1% of patients receiving levofloxacin were listed. The most common adverse reactions (≥3%) were nausea, headache, diarrhea, insomnia, constipation and dizziness.
Table 1: Common (≥1%) adverse reactions reported in clinical trials of levofloxacin
|
System/ Organ Classification
|
Adverse reactions
|
% (N=7537 )
|
|
Infections and infections
|
Candidiasis
|
1
|
|
Mental illness
|
insomnia
|
4 a
|
|
Various neurological diseases
|
headache
|
6
|
|
dizziness
|
3
|
|
Respiratory system, chest and mediastinal diseases
|
Difficulty breathing
|
1
|
|
Gastrointestinal diseases
|
nausea
|
7
|
|
diarrhea
|
5
|
|
constipation
|
3
|
|
stomach ache
|
2
|
|
Vomiting
|
2
|
|
indigestion
|
2
|
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue diseases
|
Itching rash
|
2
1
|
|
Reproductive system and breast diseases
|
Vaginitis
|
1b
|
|
Systemic diseases and various reactions at the site of administration
|
Edema,
injection site reactions variety of
chest pain
|
1
1
1
|
Note: a. N = 7274;
b. N=3758 (female).
Table 2: Less common (0.1 to 1%) adverse reactions reported in clinical trials of levofloxacin (N=7537)
|
System/ Organ Classification |
Adverse reactions
|
|
Infection and infestation
|
Genital candidiasis
|
|
Blood and lymphatic system diseases
|
Anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia
|
|
Immune system diseases
|
Allergic reaction
|
|
Metabolic and nutritional diseases
|
Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, hyperkalemia
|
|
Mental illness
|
Anxiety, agitation, confusion, depression, hallucinations, nightmares, sleep disturbancea, anorexia
|
|
Various neurological diseases
|
Shaking, convulsions, paraesthesia, dizziness, high tension, hyperkinesia, abnormal gait, drowsiness, syncope
|
|
Diseases of the respiratory tract, chest and mediastinum
|
Epistaxis
|
|
Heart organ disease
|
Cardiac arrest, palpitations, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmia
|
|
Vascular disease
|
Phlebitis
|
|
Gastrointestinal diseases
|
Gastritis, stomatitis, pancreatitis, esophagitis, gastroenteritis, glossitis, pseudomembranous/Clostridium difficile colitis
|
|
Hepatobiliary system disease
|
Abnormal liver function, increased liver enzymes, increased alkaline phosphatase
|
|
Skin and skin soft tissue diseases
|
Urticaria
|
|
Various musculoskeletal and connective tissue diseases
|
Joint pain, tendinitis, myalgia, bone pain
|
|
Kidney and urinary system diseases
|
Abnormal renal function, acute renal failure
|
Note: a. N = 7274.
In clinical trials using multiple dosing treatments, it was noted that in patients treated with quinolone antibiotics, including levofloxacin, ophthalmological abnormalities, including cataracts and multiple punctate patches of the lens, occurred. The connection between the drug and these events has not yet been established.
3. Post-marketing monitoring
The following table (Table 3) lists the adverse reactions identified in the use of levofloxacin after it was approved for marketing. Because these reactions are spontaneously reported from a variable number of people, sometimes it is impossible to reliably evaluate the incidence of these events or establish a causal relationship between drug exposure and these events.
Table 3: Post-marketing adverse drug reaction reports
|
System/ Organ Classification
|
Adverse reactions
|
|
Blood and lymphatic system diseases
|
Pancytopenia, aplastic anemia, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, eosinophilia
|
|
Immune system diseases
|
Allergic reactions, sometimes fatal, including: anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylactic shock, angioedema, serum sickness
|
|
Mental illness
|
Mental illness, paranoia, individually reported suicide attempts and suicidal thoughts
|
|
Various neurological diseases
|
Deterioration of myasthenia gravis, loss of sense of smell, loss of taste, abnormal sense of smell, dysgeusia, peripheral neuropathy, individually reported encephalopathy, abnormal electroencephalogram (EEG), dysphonia
|
|
Eye organ diseases
|
Visual impairment, including diplopia, decreased visual acuity, blurred vision, dark spots
|
|
Ear and labyrinth diseases
|
Hearing loss, tinnitus
|
|
Heart organ disease
|
Individually reported torsade de pointes ventricular tachycardia, prolonged QT interval of electrocardiogram, and tachycardia
|
|
Vascular disease
|
Vasodilation
|
|
Diseases of the respiratory tract, chest and mediastinum
|
Individually reported allergic pneumonia
|
|
Hepatobiliary system disease
|
Liver failure (including fatal disease name), hepatitis, jaundice
|
|
Skin and skin soft tissue diseases
|
Bullous rash, including: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrosis, erythema multiforme, photosensitivity/phototoxic reaction, leukocytoruptive vasculitis
|
|
Various musculoskeletal and connective tissue diseases
|
Tendon rupture, muscle injury, including rupture, rhabdomyolysis
|
|
Kidney and urinary system diseases
|
Interstitial nephritis
|
|
Systemic diseases and administration site conditions
|
Multiple organ failure, fever
|
|
Various inspections
|
Prolonged prothrombin time, increased muscle enzymes
|
【Taboo】
Patients who are allergic to this product and fluoroquinolones are contraindicated.
【Precautions】
This product is levofloxacin hydrochloride capsules, and its active ingredient is levofloxacin. The related information of levofloxacin reported in the literature is as follows:
1. Tendonitis and tendon rupture
In patients of all age groups, patients treated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics including levofloxacin may have an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture. The most common adverse reactions include Achilles Achilles tendon, and Achilles Achilles tendon requires surgical repair. Tendonitis and rupture have been reported in the shoulder, hand, biceps, thumb and other tendons. People over 60 years of age, or concurrent use of glucocorticoids, or recipients of kidney, heart, and lung transplants are at increased risk of fluoroquinolone-related tendinitis and tendon rupture. In addition to age and use of glucocorticoids, factors that can increase the risk of tendon rupture include vigorous physical activity, renal failure, and those with tendon damage such as rheumatoid arthritis in the past. It has been reported that the use of fluoroquinolones in patients without the above-mentioned risk factors causes tendonitis and tendon rupture. Tendon rupture can occur during or after the medication, and there have been reports of tendon rupture within a few months after the medication. Levofloxacin should be discontinued if the patient has pain, edema, inflammation or tendon rupture. As soon as symptoms of tendinitis or tendon rupture are found, the patient should be advised to rest and contact their medical staff to consider switching to non-quinolones.
2. Worsening of myasthenia gravis
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, including levofloxacin, can cause neuromuscular blockade, which may worsen myasthenia in patients with myasthenia gravis. Serious post-marketing adverse events, including death and the need for ventilatory support, are related to the use of fluoroquinolones in patients with myasthenia gravis. Avoid the use of levofloxacin in patients with a known history of myasthenia gravis.
3. Hypersensitivity
Patients treated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics, including levofloxacin, occasionally experience severe and sometimes fatal hypersensitivity and/or allergic reactions. These reactions often occur after the first medication. Some reactions may be accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, hypotension/shock, seizures, loss of consciousness, tingling, angioedema (including tongue, throat, pharynx, or facial edema/swelling), airway obstruction (including bronchospasm) , Shortness of breath and acute respiratory distress), dyspnea, urticaria, itching and other severe skin reactions. Levofloxacin should be stopped immediately when the rash or any other symptoms of hypersensitivity appear for the first time. Severe acute hypersensitivity needs to be treated with epinephrine, and other resuscitation measures such as oxygen inhalation, intravenous fluid replacement, use of antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management should be taken according to clinical needs.
4. Other serious and sometimes fatal adverse reactions
In rare cases, patients treated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics including levofloxacin will have serious and sometimes fatal adverse reactions. Some of these adverse reactions are hypersensitivity reactions, and some have unknown causes. These adverse reactions can be serious and usually occur after multiple medications. Clinical manifestations include one or more of the following conditions:
● Fever, rash, or severe skin reaction (such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme).
● Vasculitis, arthralgia, myalgia, serum sickness.
● Allergic pneumonia.
● Interstitial nephritis, acute renal insufficiency or renal failure.
● Hepatitis, jaundice, acute liver necrosis or liver failure.
● Anemia, including hemolytic anemia and aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia and/or other blood diseases.
When a rash or other hypersensitivity symptoms appear for the first time, the medication should be stopped immediately and corresponding supportive measures should be taken.
5. Liver toxicity
Post-marketing reports of severe liver toxicity (including acute hepatitis and fatal events) in patients receiving levofloxacin have been received. In clinical trials with more than 7,000 patients, no evidence of serious drug-related liver toxicity was found. Severe hepatotoxicity usually appears within 14 days after starting treatment, and in most cases, it appears within 6 days of starting treatment. Most cases of severe liver toxicity are not related to allergies. Most fatal liver toxicity reports are seen in patients ≥65 years of age, and most are not related to hypersensitivity. If the patient develops signs and symptoms of hepatitis, levofloxacin should be stopped immediately.
6. Central nervous system impact
There have been reports of convulsions and toxic psychosis in patients taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics including levofloxacin. Quinolone antibiotics can also cause increased intracranial pressure and central nervous system irritation, which can cause tremors, restlessness, anxiety, dizziness, confusion, hallucinations, delusions, depression, nightmares, insomnia, and in rare cases can also cause patients to produce Thoughts or actions of suicide. The above reaction may appear after the first medication. If these reactions occur in patients using levofloxacin, the drug should be discontinued immediately and appropriate treatment measures should be taken. Same as other quinolone antibiotics, if the patient is known or suspected to have a CNS disease that is prone to seizures or lowered seizure threshold (such as severe cerebral arteriosclerosis, epilepsy) or there are other risk factors that are prone to seizures or lowered seizure threshold (For example, the use of certain drugs for treatment, renal insufficiency) should be used with caution in patients with levofloxacin.
7. Diarrhea associated with Clostridium difficile
According to reports, almost all antibiotics (including levofloxacin) may cause Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD), the severity of which can range from mild diarrhea to fatal enteritis. Antibiotic treatment can change the normal flora of the colon and make Clostridium difficile multiply. Clostridium difficile can produce toxin A and toxin B, thereby promoting the occurrence of CDAD. Since antibacterial treatment of infections is difficult to work and may require colectomy, the supertoxin-producing Clostridium difficile strain can increase the morbidity and mortality of the disease. CDAD should be considered for all patients who develop diarrhea after antibiotics. According to reports, CDAD appeared after 2 months of antibiotics, so it is necessary to take a careful medical history.
If CDAD is suspected or has been diagnosed, antibacterial treatment that does not directly target Clostridium difficile needs to be stopped. According to clinical needs, appropriate fluid and dielectric management, protein supplementation, anti-Clostridium difficile treatment, and surgical treatment evaluation are performed.
8. Peripheral neuropathy
Patients treated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics including levofloxacin rarely develop polyneuropathy of sensory nerves or sensory motor axons. The lesions can involve small axons and/or large axons, leading to sensory disturbances, hypoesthesia, Pain and weakness in the touch. If the patient has neuron disease symptoms such as pain, burning, tingling, numbness and/or weakness, or other sensory disturbances such as light touch, pain, temperature, position and vibration, they should immediately stop using levofloxacin to avoid It develops into irreversible damage.
9. QT interval prolonged
Certain fluoroquinolone antibiotics, including levofloxacin, can prolong the QT interval of the electrocardiogram, and a small number of patients may have arrhythmias. Patients who spontaneously report torsade de pointes ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with quinolone antibiotics including levofloxacin during the post-marketing surveillance period are rare. Patients with known prolonged QT interval, uncorrected hypokalemia patients, and patients using class IA (quinidine, procainamide) and class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic drugs Levofloxacin should be avoided. Elderly patients are more likely to cause the effects of drug-related QT intervals.
10. Musculoskeletal diseases in pediatric patients and arthropathy effects in animals
In pediatric patients (≥6 months), levofloxacin is only suitable for the protection of anthrax inhalation (post-exposure). Compared to controls, an increase in the incidence of musculoskeletal diseases (arthralgia, arthritis, tendon disorders, and abnormal gait) was observed in pediatric patients receiving levofloxacin.
In juvenile rats and dogs, oral and intravenous administration of levofloxacin resulted in an increase in osteochondrosis. Histopathological examination of the weight-bearing joints of juvenile dogs receiving levofloxacin showed persistent cartilage damage. Other quinolones can also produce weight-bearing joint erosions and other signs of arthropathy in juvenile animals of multiple species.
11. Blood glucose disorders
Like other fluoroquinolone antibiotics, there have been reports of blood glucose disorders such as symptomatic hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. This situation mostly occurs when oral hypoglycemic drugs (such as glyburide/glyburide) or insulin are used at the same time. Diabetics. Therefore, for such patients, it is recommended that their blood glucose changes should be closely monitored. If the patient has a hypoglycemic reaction while receiving levofloxacin treatment, he should immediately stop using levofloxacin and take appropriate treatment measures.
12. Light sensitivity/phototoxicity
The use of fluoroquinolones may lead to moderate to severe photosensitivity/phototoxicity reactions after exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet light. The latter may manifest as exposure to light spots (typically including the face, the neck V area, and the extended side of the forearm, Excessive sun reactions on the back of the hand (such as sunburn, erythema, exudation, blisters, bullae, edema). Therefore, excessive exposure to the above-mentioned light sources should be avoided. If photosensitivity/phototoxicity occurs, the drug should be discontinued.
13. Production of resistant bacteria
Prescribing levofloxacin under conditions of undiagnosed or highly suspected bacterial infections and non-compliance with preventive indications will not bring benefits to patients and may increase the risk of developing resistant bacteria.
[Medicine for pregnant and lactating women]
Animal experiments have not confirmed that quinolones have teratogenic effects, but there is no clear conclusion in the research on pregnant women. In view of the fact that this medicine can cause joint disease in juvenile animals, pregnant women should not use it, and breastfeeding women should stop breastfeeding when using this product.
【Children's Medication】
The safety of this product in infants and young children under the age of 18 has not been determined. However, when this product is used in several young animals, it can cause joint disease. Therefore, it is not suitable for children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
【Medications for the Elderly】
Elderly patients often have decreased renal function, because part of this product is excreted through the kidneys, so it needs to be used in a reduced dose.
【medicine interactions】
1. Urine alkalizers can reduce the solubility of this product in urine, leading to crystaluria and nephrotoxicity.
2. When quinolone antibacterial drugs are used in combination with theophylline, the hepatic elimination of theophylline may be significantly reduced due to the competitive inhibition of the binding site of cytochrome P450, the blood elimination half-life (t1/2β) is prolonged, and the blood drug concentration is increased. , Symptoms of theophylline poisoning, such as nausea, vomiting, tremor, restlessness, agitation, convulsions, heart palpitations, etc. Although this product has little effect on the metabolism of theophylline, the blood concentration of theophylline should be measured and the dosage adjusted when used in combination.
3. The combination of this product and cyclosporine can increase the blood concentration of cyclosporine. The blood concentration of cyclosporine must be monitored and the dosage adjusted.
4. Although the anticoagulant effect of this product and the anticoagulant warfarin is small when used in combination, the prothrombin time of the patient should be closely monitored when used in combination.
5. Probenecid can reduce the secretion of this product from the renal tubules by about 50%. When used in combination, it can cause toxicity due to the increase in blood concentration of this product.
6. This product can interfere with the metabolism of caffeine, resulting in reduced caffeine elimination, prolonged blood elimination half-life (t1/2β), and may cause central nervous system toxicity.
7. Antacids and iron containing aluminum and magnesium can reduce the oral absorption of this product and should not be used in combination.
8. When this product is used in combination with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug fenbufen, convulsions occasionally occur, so it is not suitable to use it in combination with fenbufen.
【Overdose】
The experiment has not been carried out and there is no reliable reference.
【Pharmacology and Toxicology】
This product has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect, strong antibacterial effect, against most Enterobacteriaceae bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Shigella and Haemophilus influenzae, Gram-negative bacteria such as Legionella pneumoniae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae have strong antibacterial activity. It also has antibacterial effect on Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes and other gram-positive bacteria, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae, but it has poor effect on anaerobic bacteria and Enterococcus.
This product is the L-body of ofloxacin, and its in vitro antibacterial activity is about twice that of ofloxacin. Its mechanism of action is to prevent bacterial DNA synthesis and replication by inhibiting the activity of bacterial DNA gyrase, leading to bacterial death.
【Pharmacokinetics】
After oral administration, the absorption is complete. After a single oral dose of 0.2g, the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) is about 1.6 mg/L, and the peak time (Tmax) is about 1 hour. The blood elimination half-life (t1/2β) is about 6 hours. The protein binding rate is about 30% to 40%.
After absorption, the product is widely distributed to various tissues and body fluids. The ratio of the concentration in tissues and body fluids such as tonsils, prostate tissue, sputum, tears, women's reproductive tract tissue, skin and saliva to blood concentration is about 1.1-2.1. between.
This product is mainly excreted from the kidneys in its original form, with little metabolism in the body. Urinary excretion within 48 hours of oral administration is about 80% to 90% of the dose. A small amount of this product is excreted from the feces in its original form, and the cumulative excretion within 72 hours after administration is less than 4% of the administered amount.
【Storage】
Shading, sealed and preserved.
【package】
Aluminum-plastic blister packaging, 10 tablets/plate; carton packaging, 1 plate/box.
【Validity Period】
24 months
【Executive Standard】
"Chinese Pharmacopoeia" 2015 Edition Two
【Approval Number】
National Medicine Standard H20010614
【manufacturer】
Company Name: Shenyang Hongqi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Production address: No. 6, Xinluo Street, Hunnan New District, Shenyang City
Postal Code: 110179
Phone number: 024-23786260 23786261
Fax number: 024-23786263
Website: www.hongqipharma.com